
Replication is the process by which a cell duplicates its DNA before division. In humans, for example, each parent cell must copy its entire six billion base pairs of DNA before undergoing mitosis. After the discovery of DNA structure the main objectives of scientists were to know the process of replication and how do the DAN replicate The Replication of Deoxyribonucleic Acid (DNA) and Ribonucleic Acid (RNA) DNA replication is when a cell divides and every new cell has a copy of the original cell’s genetic information. This allows it to synthesize the proteins to build cellular parts and metabolize. Replication of DNA happens during the interphase of a cell cycle The first step to DNA replication is the unwinding of the double helix with the help of an enyme called helicase. Once unwound, the DNA unzips and the bonded nucleotides are separated. In the next stage, an enzyme called DNA polymerase is important
Dna Replication Essay examples - Words | Bartleby
After that Fred Griffith worked with virulent S and non-virulent R strain. He studied Streptococcus pneumonia, the bacterium that causes pneumonia. The smooth dna replication essay core of the bacterium is known as strain S and the rough outer core dna replication essay the bacterium is known as strain R.
Griffith injected both strains into mice dna replication essay found that dna replication essay strain S bacteria were deadly. Then he injected dna replication essay strain R bacteria and strain S bacteria that had been killed by heat but the mice died and he found a bug that living strain S bugs suddenly appeared. He concluded that something from the dead strain S bacteria and converted strain R bacteria into strain S bugs, dna replication essay.
He called it the "transforming principle. After that in Oswald T. Avery put killed strain S in a test tube. Thus he concluded that DNA was the transforming agent. After that in Edwin Chargaff an Austrian biochemist studied the chemical composition of DNA molecule and had revealed that it contained a type of sugar called deoxyribose, plus a phosphate group and four different molecules or bases called adenine, thymine, guanine and cytosine.
DNA stands for Deoxyribonucleic acid. It is the hereditary material in humans and almost all other organisms. Most DNA is located in the nucleus of the cell which is known as nuclear DNA, but a small amount of DNA can also be found in the mitochondria, known as mitochondrial DNA or mtDNA.
Human DNA consists of about 3 billion bases, and about 99 percent of those bases are same in all people. The order or sequence of these bases determines the information available for building and maintaining of an organism. Each pair form a unit thus called base pairs. Basically DNA is made up of subunits called nucleotides. Each base is also attached to a sugar molecule and dna replication essay phosphate molecule.
This sugar molecule, phosphate molecule and a base pair joined together which is called a nucleotide. So a nucleotide is made up of following things:. These nucleotides are arranged into two long strands forming a spiral called a double helix.
DNA structure is made up of two coiled strands called double helix in which sides are made up of pentose sugar deoxyribose bonded to phosphate groups by phosphodiester bonds and their center is made up of nitrogen bases bonded together by weak hydrogen bonds. Most DNA has a right-hand twist with 10 base pairs in a complete turn. Left twisted DNA is called Z-DNA or southpaw DNA.
Hot spots occur where right and left twisted DNA meat producing mountains. Synthesis phase or "S phase" occurs during the interphase of a cell cycle between the G1 and G2 stages. During synthesis phase, DNA replication takes place, dna replication essay. DNA molecules "unzip" and each old strand attracts free nucleotides forming complementary new strands, leaving two strands of DNA identical to the original strand of DNA. In humans, for example, each parent cell must copy its entire six billion base pairs of DNA before undergoing mitosis, dna replication essay.
After the discovery of DNA structure the main objectives of scientists were to know the process of replication and how do the DAN replicate. For this purpose the scientists proposed three models of DNA. They are:. According to the conservative replication model, the entire original DNA double helix serves as a template for a new double helix, dna replication essay that each round of cell division produces one daughter cell with a completely new DNA double helix and another daughter cell with a completely intact old original DNA double helix.
In the dispersive replication model, the original DNA double helix breaks apart into fragments and each fragment then serves as a template for a new DNA fragment.
As a result, every cell division produces two cells with varying amounts of old and new DNA. According dna replication essay the semi-conservative replication model, the two original DNA strands i.
When these three models were first proposed, scientists had few clues about the process occurring at the molecular level during DNA replication.
Fortunately, the models yielded different predictions about the distribution of old versus new DNA in newly divided cells. These predictions were as follows:. Dna replication essay to the semi-conservative model, after one round of replication, every new DNA double helix would be a hybrid that consisted of one strand of old DNA bound to one strand of newly synthesized DNA. Then, during the second round of replication, the hybrids would separate, and each strand would pair with a newly synthesized strand.
Afterward, only half of the new DNA double helices would be hybrids; the other half would be completely new. Every successive round of replication therefore would result in fewer hybrids and more completely new double helices. According to the conservative model, after one round of replication, half of the new DNA double helices would be composed of completely old, original DNA, and the other half would be completely new. Then, during the second round of replication, each double helix would be copied in its entirety.
Afterward, dna replication essay, one-quarter of the double helices would be completely old, and three-quarters would be completely new. Thus, each successive round of replication would result in a greater proportion of completely new DNA double helices, while the number of completely original DNA double helices would remain constant.
According to the dispersive model, every round of replication would result in hybrids, or DNA double helices that are part original DNA and part new DNA. Each subsequent round of replication would then produce double helices with greater amounts of new DNA.
Matthew Meselson and Franklin Stahl were well familiar with these three predictions, and they reasoned that if there were a way to distinguish old versus new DNA, it should be dna replication essay to test each prediction.
As they were aware of previous studies that had relied on isotope labels as a mode to differentiate between parental and progeny molecules, they decided to see whether the same technique could be used to differentiate between parental and progeny DNA. As their sedimentation method they used a technique known as cesium chloride CsCl equilibrium density gradient centrifugation. Meselson and Stahl opted for nitrogen because it is an essential component of DNA; therefore, whenever a cell divides and its DNA replicates, it incorporates new N atoms into the DNA of its daughter cells, depending on which model was correct.
If several different density species of DNA are present," they predicted, "each will form a band at the position where the density of the CsCl solution is equal to the density of that species, dna replication essay.
In this way, DNA labeled with heavy nitrogen 15N may be resolved from unlabeled DNA", dna replication essay. They then continued their experiment by growing a culture of E. coli bacteria in a medium that had the heavier 15N in the form of 15N-labeled ammonium chloride as its only source of nitrogen.
The bacteria divide will contain 15N. Then they changed the medium to one containing only 14N-labeled ammonium salts as the sole nitrogen source. So, from that point onward, every new strand of DNA would be built with 14N rather than 15N. Just before the addition of 14N and periodically thereafter, as the bacterial cells grew and replicated Meselson and Stahl sampled DNA for use in equilibrium density gradient centrifugation to determine how much 15N from the original or old DNA versus 14N from the new DNA was present.
For the centrifugation procedure, they mixed the DNA samples with a solution of cesium chloride and then centrifuged the samples for enough time to allow the heavier 15N and lighter 14N DNA to move to different positions in the centrifuge tube. By centrifugation, the scientists found that DNA composed entirely of 15N-labeled DNA i. Following a single round of replication, the DNA again formed a single distinct band, dna replication essay, but the band was located in a different position along the centrifugation gradient.
Specifically, it was found midway between where all the 15N and the entire 14N DNA would have migrated, in other words, halfway between "heavy" and "light". Based on these findings, the scientists were immediately able to exclude the conservative model of replication as a possibility. After all, if DNA replicated conservatively, there should have been two distinct bands after a single round of replication; half of the new DNA would have migrated to the same position as it did before the culture was transferred to the 14N-containing medium i.
That left the scientists with only two options: either DNA replicated semi-conservatively, as Watson and Crick had predicted, or it replicated dispersively. To differentiate between the two, dna replication essay, Meselson and Stahl had to let the cells divide again and then sample the DNA after a second round of replication.
After that second round of replication, the scientists found that the DNA separated into two distinct bands: one in a position where DNA containing only 14N would be expected to migrate, and the other in a position where hybrid DNA containing half 14N and half 15N would be expected to migrate. The scientists continued to observe the same two bands after several successive rounds of replication.
These results were consistent with the semi-conservative model of replication and the reality that, when Dna replication essay replicated, each dna replication essay double helix was built with one old strand and one new strand. If the dispersive model were the correct model, the scientists would have continued to observe only a single band after every round of replication, dna replication essay. Semi-conservative replication made sense in light of the double helix structural model of DNA, in particular its complementary nature and the fact that adenine always pairs with thymine and cytosine always pairs with guanine, dna replication essay.
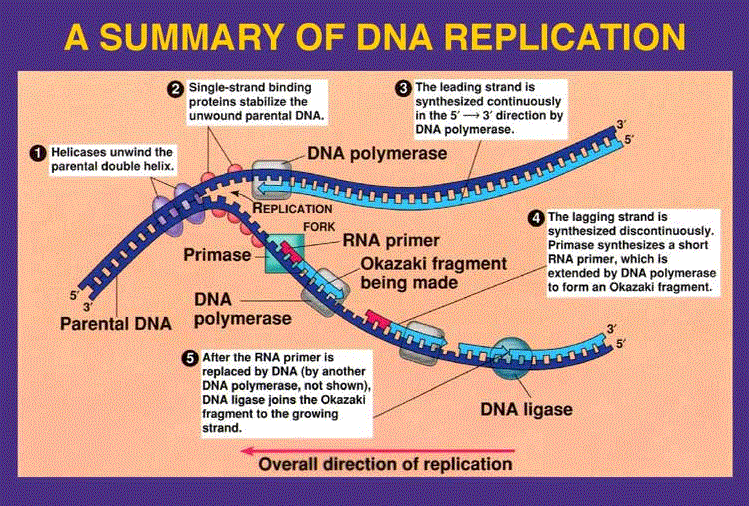
Looking at this model, it is easy to imagine that during replication, each strand serves as a template for the synthesis of a new strand, with complementary bases being added in the order indicated. DNA replication is possible because of the action of specific enzymes on DNA strands. Following are the enzymes which participate in DNA replication, dna replication essay. Its function is to glue down the pieces of DNA created by DNA polymerase I and III.
It also joins the Okazaki fragments of the lagging strand of DNA. It is the main enzyme that is responsible for the DNA replication. It is a six protein complex arranged in a ring form. Its function is to unwind the double stranded DNA Helix and prying apart the double strands so primase, polymerase and ligase could act upon single strands of DNA.
These proteins work together to bind the individual dna replication essay in the DNA double stranded helix and aid the helicases in opening it up into single strands. They are particularly useful in stabilizing the unwounded single-stranded conformation. It causes the length of a telomeric DNA to increase by adding repetitive nucleotide sequences to the ends of eukaryotic chromosomes. It is the first stage and starting point of DNA replication. It has the following aspects and enzymes involved in it.
Initiation always starts with replication origin. In order to begin the DNA replication the double stranded DNA helix must be opened. The site where first replication process occurs is called as replication origins. DNA helicases are used to unwind the DNA into two single strands. The hydrogen bonds between the complementary nucleotide bases break down, dna replication essay. As a result the coiled double helix structure changes to two single DNA strands, dna replication essay.
Single- strand DNA binding proteins along with helicase acts on DNA strands and keep them separated and stabilized as the newly unwound DNA strands might have ability to twist again forming hydrogen bonds with complementary nucleotide bases. After such enzymes action replication bubble is created.
It forms at multiple sites along the length of DNA. It catalyzes the replication process, dna replication essay.
The open structure of DNA is often referred as replication fork, dna replication essay.
Notes - DNA Structure \u0026 Replication
, time: 17:44The History Of Dna Replication Biology Essay
The first step to DNA replication is the unwinding of the double helix with the help of an enyme called helicase. Once unwound, the DNA unzips and the bonded nucleotides are separated. In the next stage, an enzyme called DNA polymerase is important Replication is the process by which a cell duplicates its DNA before division. In humans, for example, each parent cell must copy its entire six billion base pairs of DNA before undergoing mitosis. After the discovery of DNA structure the main objectives of scientists were to know the process of replication and how do the DAN replicate Origin Of Replication Is The Starting Point Of Dna Replication Essay Words | 7 Pages. Exam 2 - Tao Xu (Nov) Origin of replication is the starting point of DNA replication. It cannot replicate in the host cells without this site. Antibiotic resistance gene can be served as a select agent to find the right clone and then improve the

No comments:
Post a Comment